
Industry: Transportation
Manufacturers: Still Doubting Automation
In today’s manufacturing sectors, companies continually face various pressing challenges. Labor shortages and rising labor costs require innovative solutions to maintain productivity with fewer workers.
Additionally, relentless inflation continues to put pressure on raw material costs, thus reducing margins. Manufacturers are also competing against tight production deadlines, driven by the imperative for shorter time-to-market, a direct consequence of increasing global competition.
To overcome these widespread issues, many executives and factory managers are turning to automation and metrology solutions. However, they seek to leverage these technologies even further to maximize their investments. So, what are the possible next steps?
This article provides insights on how manufacturing companies can harness the potential of 3D scanners in automated environments. It also offers guidance for adopting approaches that balance initial technology investments with future scalability toward full automation.
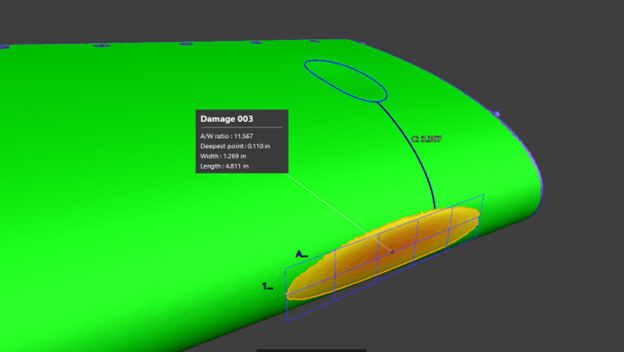
Despite widespread recognition of automation as an indispensable factor in modern manufacturing, manufacturers are still hesitant to fully adopt automated production lines. This reluctance is rooted in organizational culture and operational considerations.
The Perception of Automation is Too Complex
For many manufacturers, the perceived complexity of automation acts as a deterrent. The notion that automation requires a radical overhaul of existing processes and equipment fosters fear of the unknown. There is a prevailing concern that introducing sophisticated systems like robots and cobots will lead to job losses and a significant learning curve for employees.
Psychological resistance to change is further exacerbated by the misconception that automation is an all-or-nothing proposition rather than a scalable process that can be integrated gradually and managed with familiar tools.
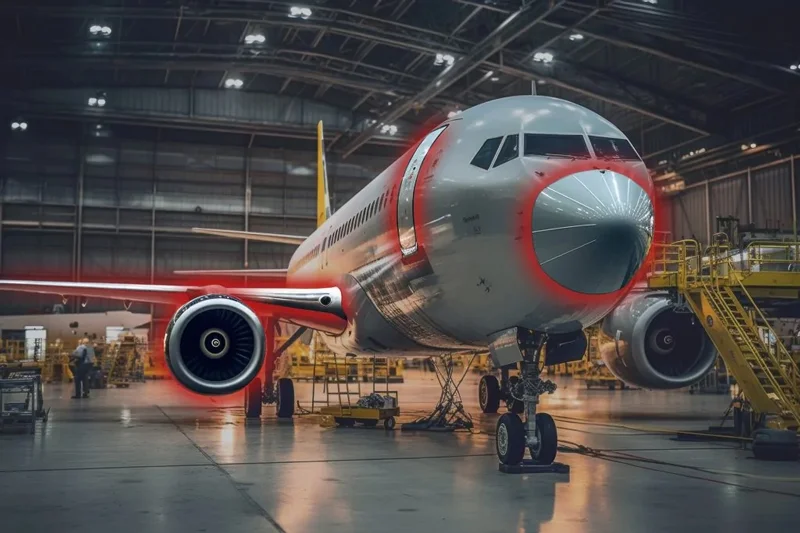

Lack of Internal Expertise
Another barrier to automation is the apparent lack of internal expertise. Small and medium-sized manufacturers, in particular, may not have the resources to maintain a dedicated IT department capable of implementing and maintaining advanced automation systems. They may assume that without specialists to guide the automation process, the chances of successful implementation decrease, preventing them from taking initial steps, despite the availability of more user-friendly automation tools.
Misconceptions About Cost Implications
A misunderstanding of the costs involved amplifies doubts about automation. Manufacturers tend to focus on the immediate financial outlay while overlooking or underestimating the potential return on investment, which includes long-term savings and efficiency gains. This narrow view of finances obscures the true value of automation and its ability to optimize operations and reduce costs over time.
The Integration of 3D Scanners as the First Controlled Step Toward Automation
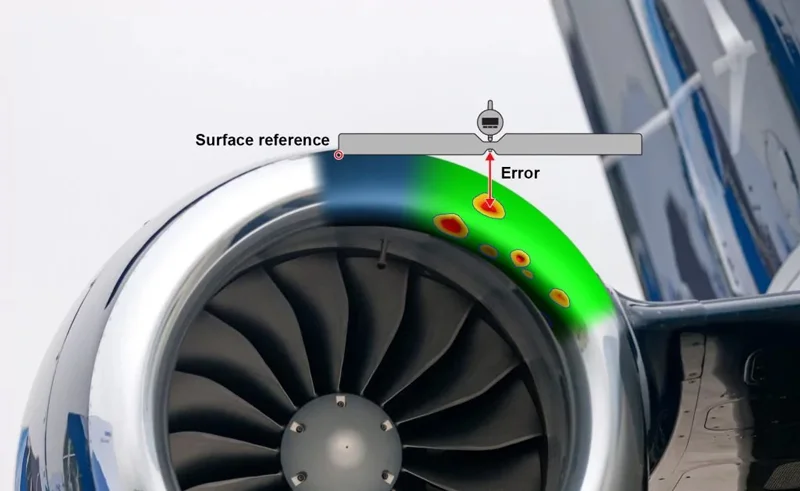
3D metrology-grade measurement solutions stand out for their versatility. They can be used at various stages of the manufacturing process, including product design and development, quality control and assurance, reverse engineering, and directly on production lines.
The Role of 3D Scanning in Bridging the Gap in Automated Manufacturing
During the preliminary phase, 3D scanners help create accurate and detailed design models, laying the foundation for quality. As products move through the manufacturing cycle, 3D scanners can be used for evaluations and quality control on the fly, transitioning easily from manual and practical operations to semi-automated processes.

This adaptability offers manufacturers a tangible starting point for automation, allowing them to begin gradually and progress without the need for a complete overhaul of automation.
For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), where each investment has even more weight in terms of return, 3D scanning technologies can be a cost-effective solution for taking a step toward automation without immediately adopting a fully automated system. This enables SMEs to gradually increase their automation capabilities along with their growth and financial comfort level. By implementing 3D scanning, these companies can harness the benefits of automation, such as greater precision and speed in production, without the large-scale investment that larger, more complex robotic systems would require.
The Inherent Scalability of 3D Scanning Technology
Perhaps the most compelling argument for incorporating 3D scanning technology is its inherent scalability. It’s a future-ready investment that supports a company’s growth trajectory. As businesses evolve and market demands change, 3D scanning systems can scale to meet increased production needs or extend capabilities to new product lines.
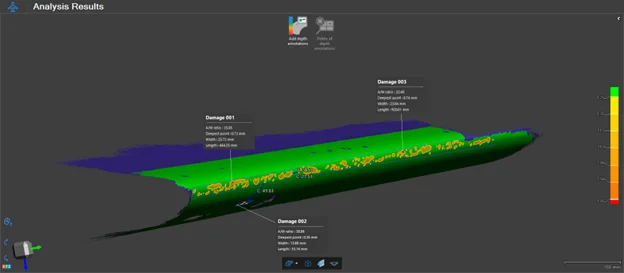
In Summary: 3D Scanners Assist in the Transition Toward Automation
For manufacturers facing the pressures of modern markets, starting with a versatile and upgradable 3D scanning solution provides a strategic path forward.
By selecting the right 3D measurement technology and implementation approach, companies can enhance their product development and quality control processes, improve efficiency, mitigate upfront costs, and lay the foundation for future automation.
A strategic investment in 3D scanning not only addresses current manufacturers’ needs but also sets the stage for progressive growth, ensuring they can adapt and thrive with emerging automation technologies.
Choosing the Right 3D Scanner
When selecting 3D scanning equipment, it is important to consider key factors to ensure the solution chosen can meet your company’s needs both now and in the future. These factors include:
- Scalability: It’s best to choose technology that offers both portable and automatable options. This allows for an initial investment in portable devices that can be expanded into automated systems as needs evolve and budgets permit.
- Versatility: The technology should handle complex geometries and various materials without requiring extensive preparation, making it suitable for a wide range of applications and ensuring its long-term usefulness.
- Speed and Precision: These are essential to maintain productivity and quality. The chosen technology should provide fast data acquisition and high precision to meet strict tolerances and quality standards.
- Software Compatibility: It’s essential to seek solutions that work seamlessly with external simulation and metrology software, allowing for efficient data transfer and use throughout the manufacturing process.
- Provider Expertise: When selecting a 3D scanning manufacturer, it’s important to choose one with extensive knowledge of both hardware and software. This ensures access to optimized support when addressing the most challenging production workflows. Additionally, you should inquire whether the provider has previously worked on automation projects with their 3D scanners or if they offer dedicated 3D measurement solutions for automated processes, such as quality control. It’s also worth checking if the provider offers integration services for their technologies in production environments.








